Exploring the Characteristics of Cloud Computing (2024)

/ Unlock the potential of cloud computing! Explore its characteristics and learn why it’s transforming the digital landscape.
By Nilesh Badwar.
Date: 23 Dec, 2023, 12:34 PM IST
In today’s digitally interconnected world, cloud computing has emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing how individuals and organizations access and manage their computing resources. The realm of cloud computing is not new, dating back to early discussions of distributed computing as far back as 1993.
However, it has evolved into a technological powerhouse, driven by industry giants such as Amazon, Google, and Microsoft. In this article, we embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of cloud computing by examining its defining characteristics, which have propelled it into the mainstream of modern technology.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a concept that entails the dynamic provisioning of a broad spectrum of computing resources and services over the internet. These resources encompass storage, applications, networking capabilities, databases, software tools, development environments, processing power, and more. This provisioning is orchestrated by entities known as Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) who serve as the custodians of these digital assets, making them accessible to users worldwide.
What distinguishes cloud computing from conventional computing is its capacity to deliver these services with minimal user management or service-provider interaction. In essence, cloud computing can be aptly described as internet-based computing, where data, applications, and services reside on remote servers rather than being tethered to individual devices or local storage.
Cloud service providers operate vast data centers housing these services, extending them to users who pay based on usage or through monthly subscriptions. This model bestows a remarkable degree of computing power and storage capacity upon users, eliminating the intricacies of hands-on management. It operates in a manner analogous to how internet service providers seamlessly deliver internet access to end-users without requiring them to comprehend the underlying infrastructure.
The burgeoning demand for extensive storage, both by enterprises and individuals, has propelled cloud computing to the forefront. Leading companies vie with one another to provide an ever-expanding array of features coupled with storage services.
Cloud Service Models and Key Players
Cloud computing offers a trio of prominent service models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This model delivers essential infrastructure resources, including physical computing resources, security, scaling, storage, and networking, to users.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS furnishes users with a comprehensive development environment encompassing an operating system, database, Integrated Development Environment (IDE), and more, streamlining application development and deployment.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS grants users access to applications and software from any location, often via a web browser.
Distinguished cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, IBM Cloud, and Salesforce offer these services, catering to diverse business and individual needs.
Before we dive into the defining characteristics of cloud computing, it’s essential to understand why this paradigm has witnessed such widespread adoption:
- Cost Reduction: Cloud computing significantly curtails hardware and software expenses, with users paying solely for resources used on a subscription basis.
- Accessibility: Cloud services are universally accessible, facilitating work and data access from any device with an internet connection.
- Scalability: Cloud resources are extraordinarily scalable, permitting users to adjust capacity in response to demand, ensuring cost optimization.
- Security: Cloud service providers invest substantially in security measures, ensuring robust protection against data breaches and security threats.
- Reliability: Cloud storage is renowned for its reliability, with streamlined backup and data recovery options.
- Efficiency and Productivity: Cloud services simplify access to applications and data, enhancing organizational productivity by alleviating infrastructure management burdens.
With this foundational understanding, let us now explore the defining characteristics that underpin the transformative power of cloud computing.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
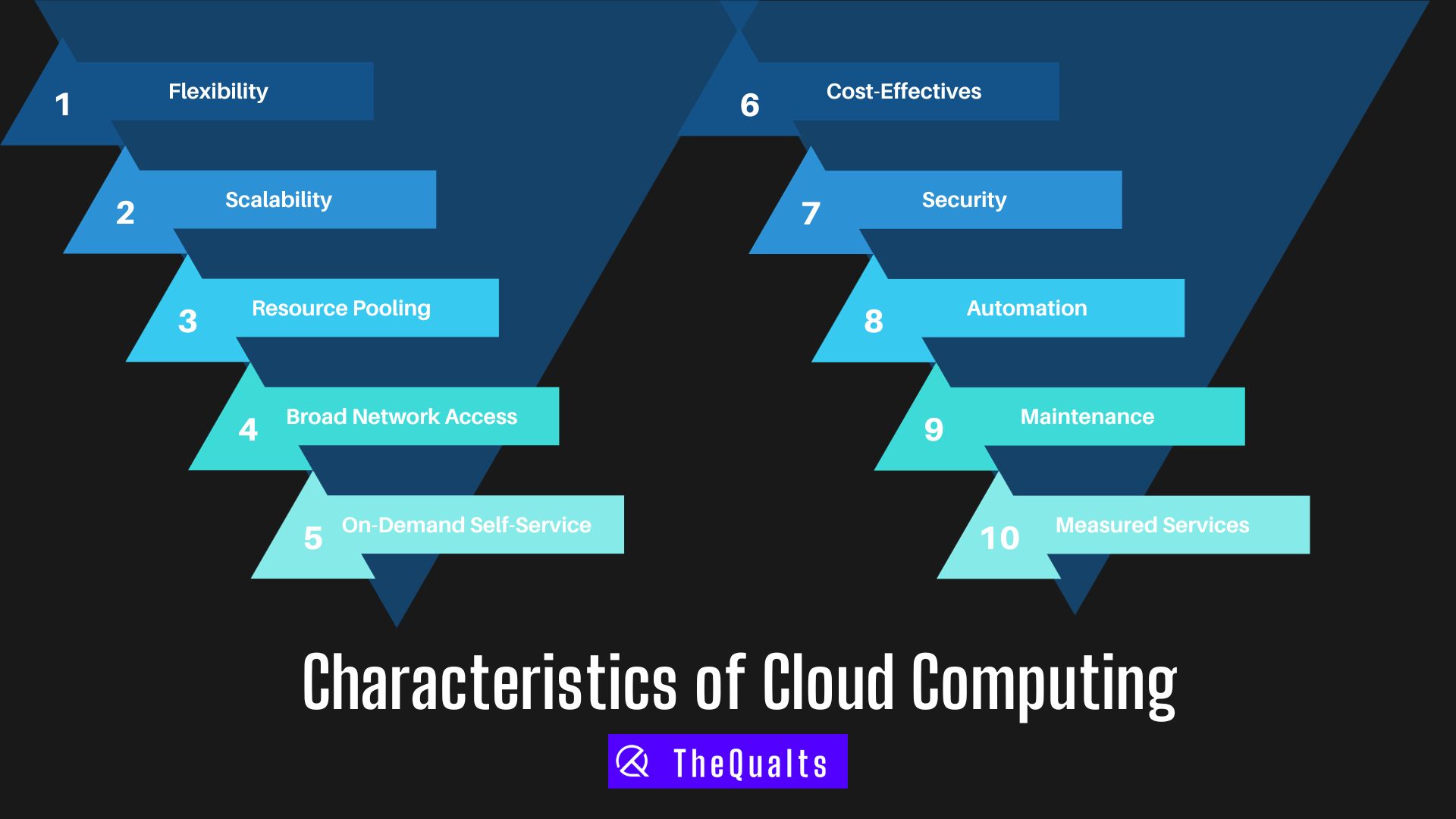
Flexibility: Cloud computing enables users to access data and services from internet-enabled devices, fostering easy sharing and collaboration. Organizations often prefer cloud storage for its cost savings and collaborative advantages.
Scalability: The cloud’s ability to expand or shrink resources according to demand is one of its standout features. It ensures cost-effectiveness and adapts to fluctuating workloads seamlessly.
Resource Pooling: Cloud providers securely pool computing resources, sharing them among clients while ensuring isolation. This multi-tenant approach optimizes resource utilization without compromising security.
Broad Network Access: Cloud computing knows no geographical boundaries, offering global access via the internet. Users can access files and applications from anywhere, provided they have an internet connection and a device.
On-Demand Self-Service: Cloud services empower users to manage their resources, making them their own administrators. Users can monitor consumption, select tools, and utilize resources directly from the cloud portal, promoting responsible resource use.
Cost-Effective: Cloud computing operates on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing users to control costs by monitoring and adjusting resource usage. It eliminates upfront hardware and software costs, making it especially attractive for startups.
Security: Cloud providers prioritize data security, employing encryption, user authentication, and safeguards against breaches. Physical security measures protect data centers, and automated backups ensure data resilience.
Automation: Automation is integral to cloud infrastructure, reducing human interaction in configuration, maintenance, and monitoring. This automation contributes to the efficiency and rapid expansion of cloud services.
Maintenance: Cloud maintenance is streamlined and often automated, requiring minimal additional costs. Upgrades in infrastructure and software continually improve the ease and affordability of maintenance.
Measured Services: Cloud providers track and bill users based on resource consumption, offering a transparent pay-as-you-go subscription model. This benefits both users, who can monitor their usage, and providers, who can manage resources efficiently.
Resilience: Cloud computing systems are designed to recover from interruptions and disasters. Redundancy, backup nodes, and advanced recovery methods ensure data is protected even in adverse scenarios.
In conclusion, cloud computing has become a driving force in the technology landscape due to its flexibility, scalability, cost-effectiveness, security, and numerous other characteristics. As the demand for cloud services continues to rise, cloud providers will likely innovate further to meet the evolving needs of businesses and individuals alike, solidifying cloud computing’s place as a pivotal technological advancement in the digital age.
